-
Github
iPsychCNV is an open source R package project. People are welcome to give suggestions, code new functions and/or improve existing ones. The source code is available at Github .
-

About iPsychCNV
iPsychCNV is a method to find copy number variation from amplified DNA from dried blood spots on Illumina SNP array. It is designed to handle large variation on Log R ratio, and uses B allele frequency to improve CNV calls. iPsychCNV is an open source project on Github
-

About iPSYCH
The project will study five specific mental disorders; autism, ADHD, schizophrenia, bipolar disorder and depression. All disorders are associated with major human and societal costs all over the world. The iPSYCH project will study these disorders from many different angles, ranging from genes and cells to population studies, from fetus to adult, from cause to symptoms of the disorder, and this knowledge will be combined in new ways across scientific fields, visit iPSYCH.
Challenges
What are dried blood spots (DBS) ?
Dried blood spot testing (DBS) is a form of biosampling where blood samples are blotted and dried on filter paper. The dried samples can easily be shipped to an analytical laboratory and analysed using various methods such as DNA amplification or HPLC.
Dried blood spot specimens are collected by applying a few drops of blood, drawn by lancet from the finger, heel or toe, onto specially manufactured absorbent filter paper. The blood is allowed to thoroughly saturate the paper and is air dried for several hours. Specimens are stored in low gas-permeability plastic bags with desiccant added to reduce humidity, and may be kept at ambient temperature, even in tropical climates.
The reason for stability of DNA, RNA or protein could be attributed to the fact that the biological material binds to the matrix of the filter paper and the process of drying excludes water which is an important factor necessary for protease or nuclease to act. Binding of the biological material also binds several inhibitors which may interfere with various nucleic acid amplification methods. From wikipedia: Dried blood spots.
The iPSYCH project genotyped around 80.000 Danish individuals from dried blood spots using the Illumina SNP chip platform. Here we show examples of some challenges encountered by copy number variation detection methods.
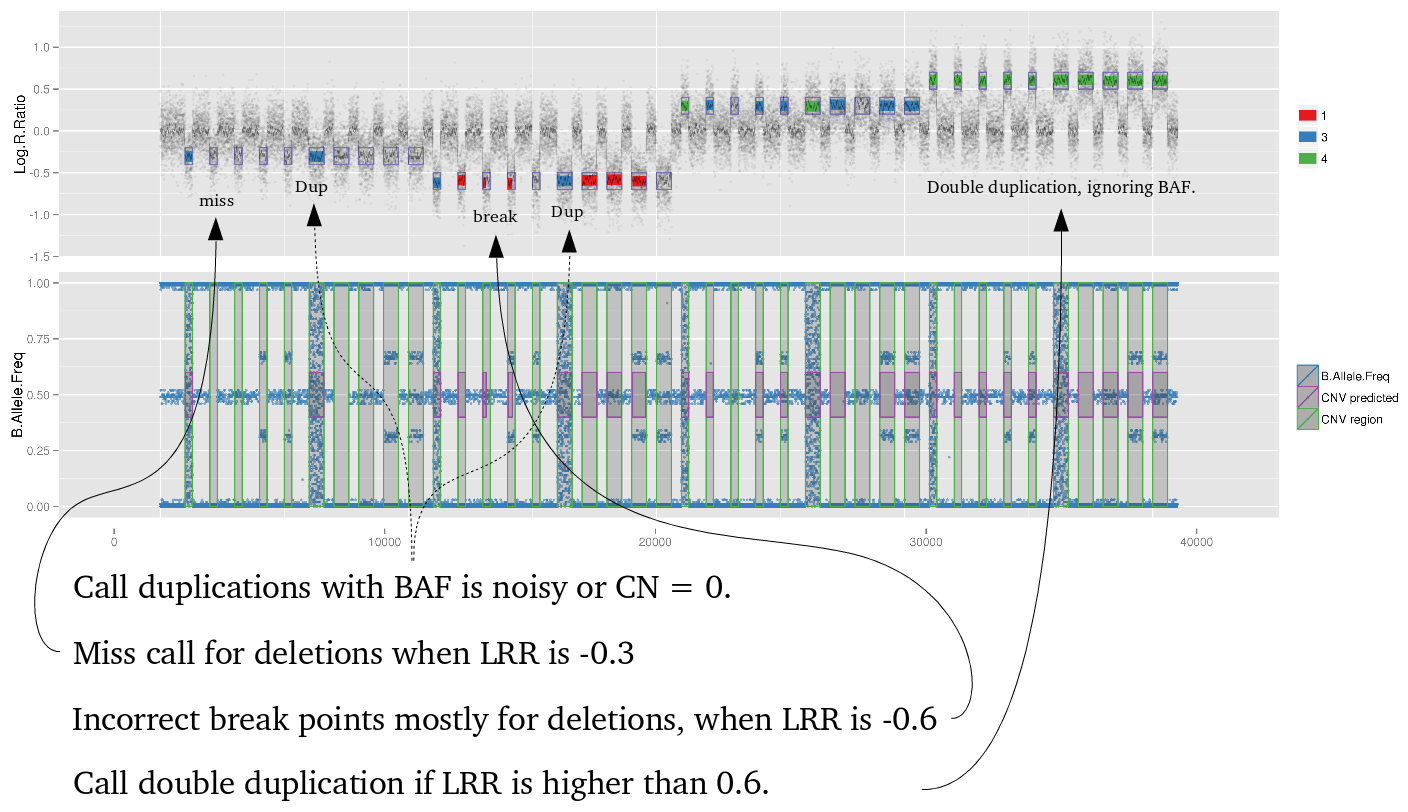
High standard deviation from Log R ratio (LRR).
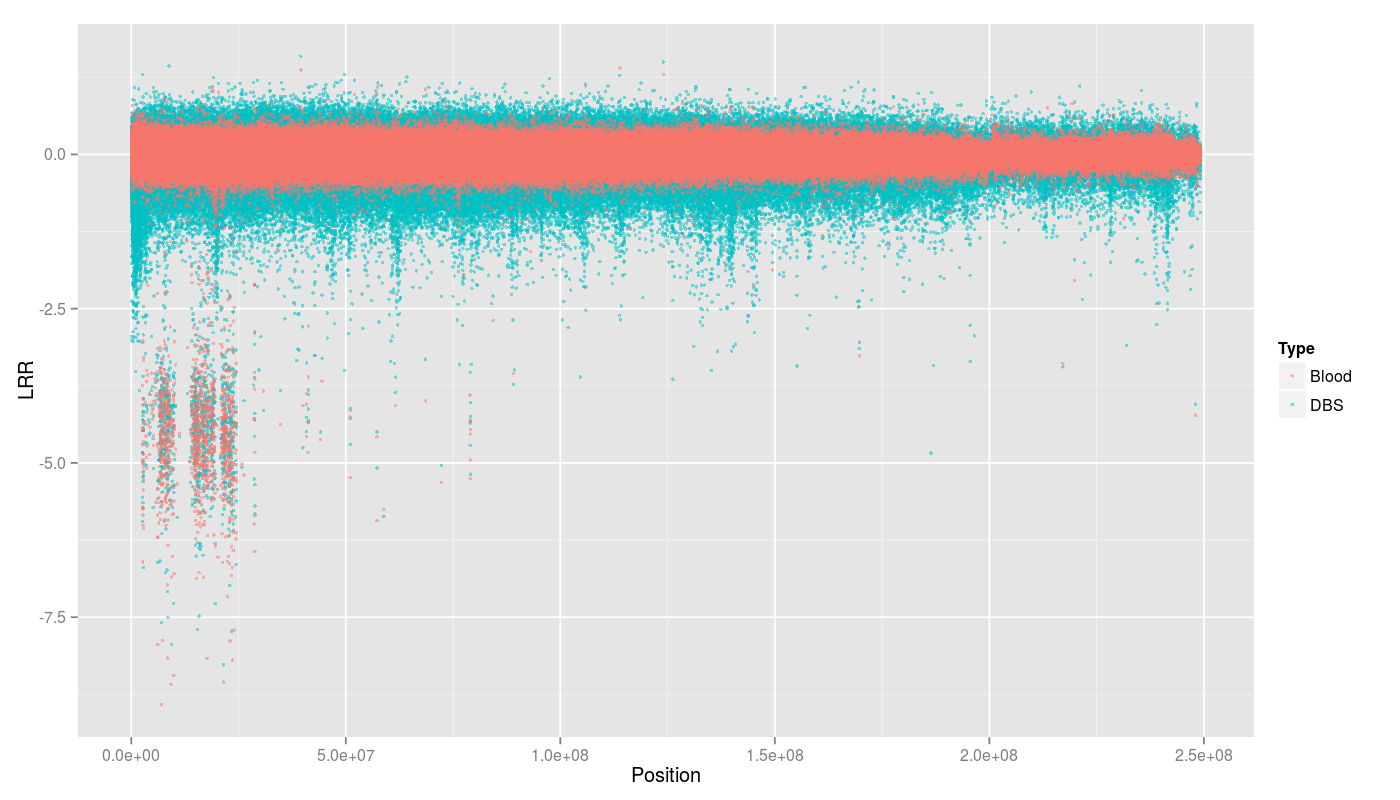
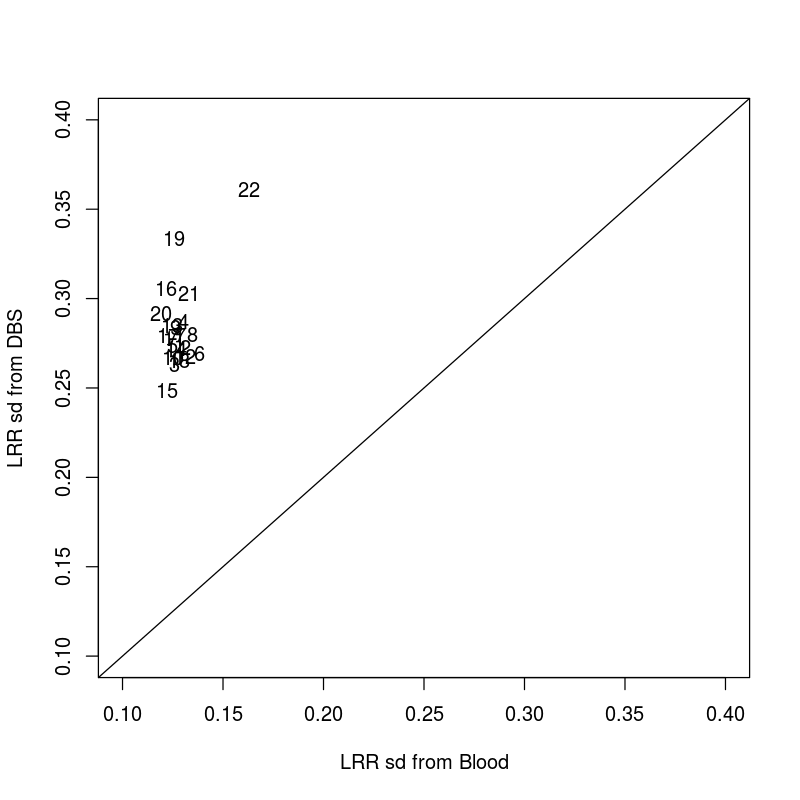
BDS and blood standard deviation Log R ratio.
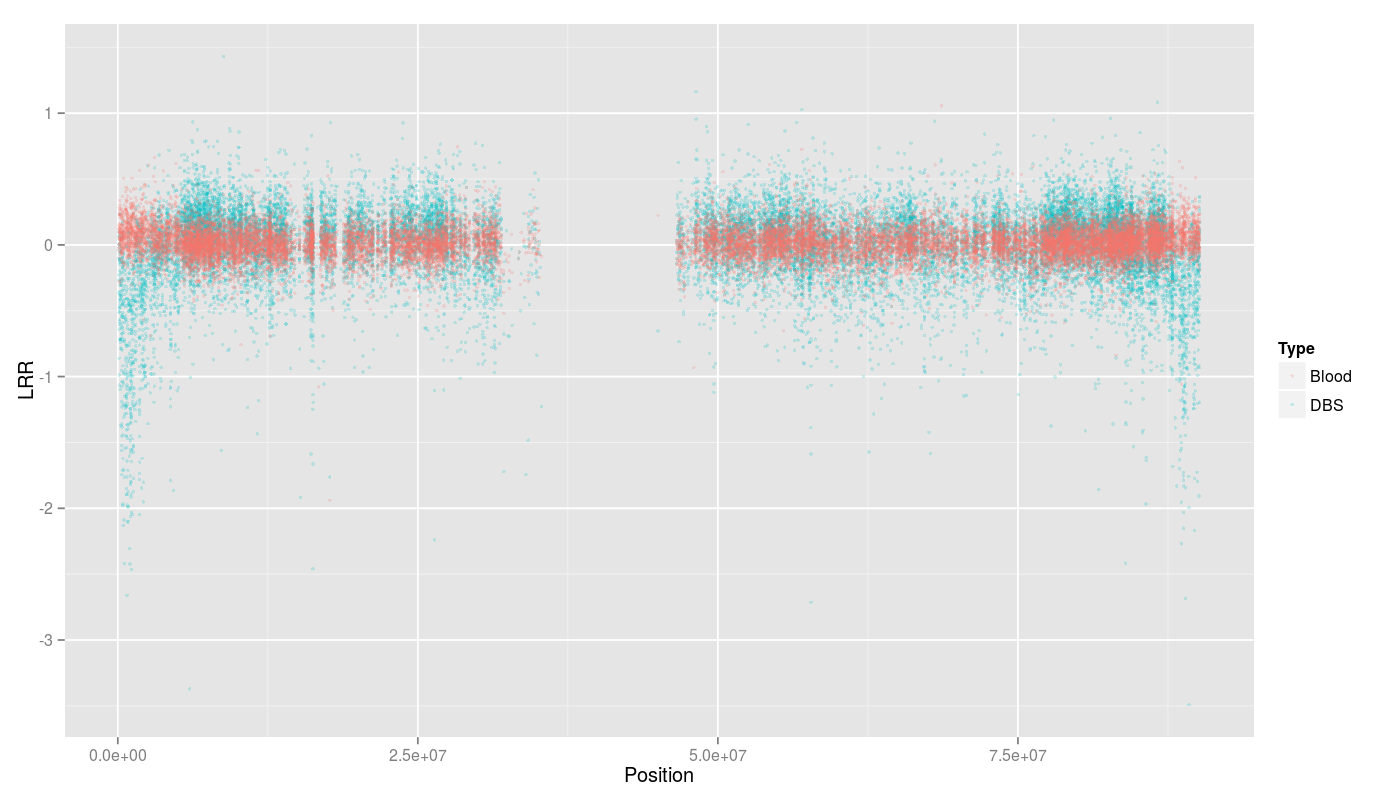
Low LRR signal on telomere and centromere regions from chromosome 16.
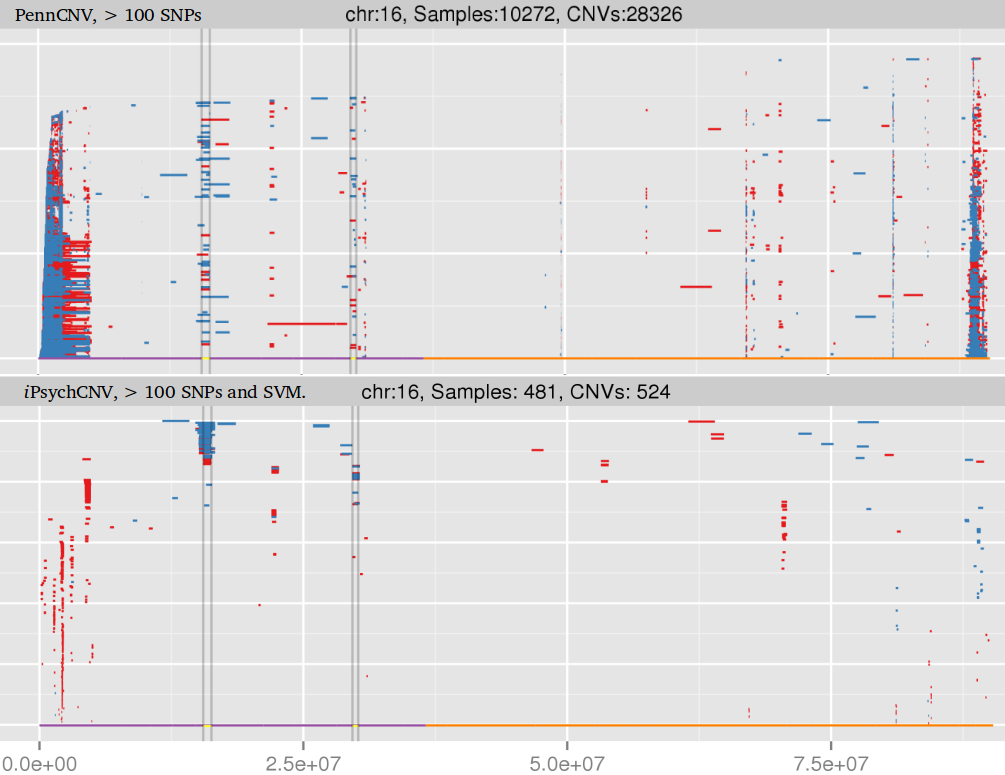
Blood and dried blood spots: iPsychCNV and PennCNV prediction.
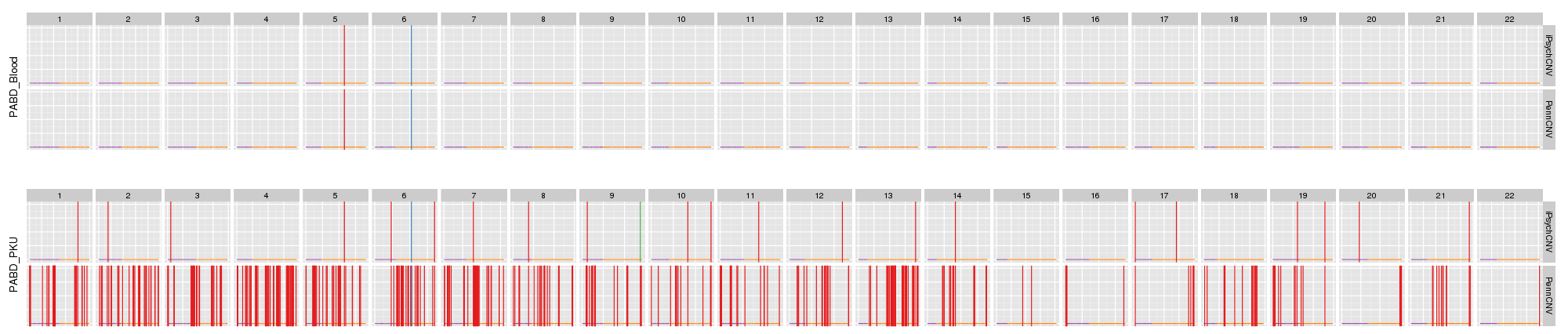
Example of single CNV plot false positive calls.
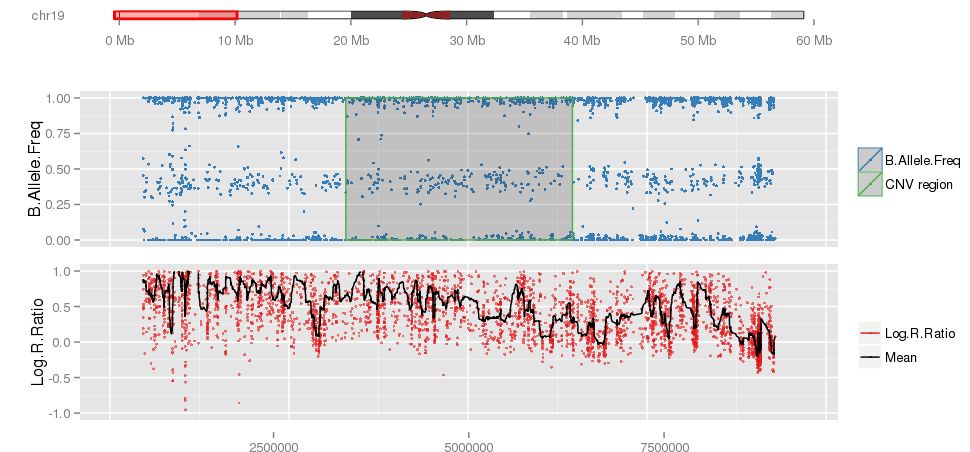
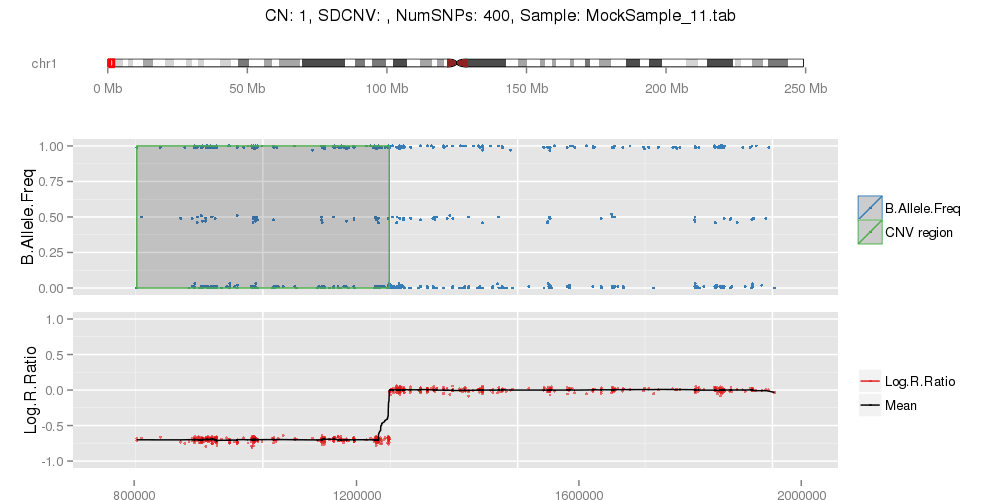
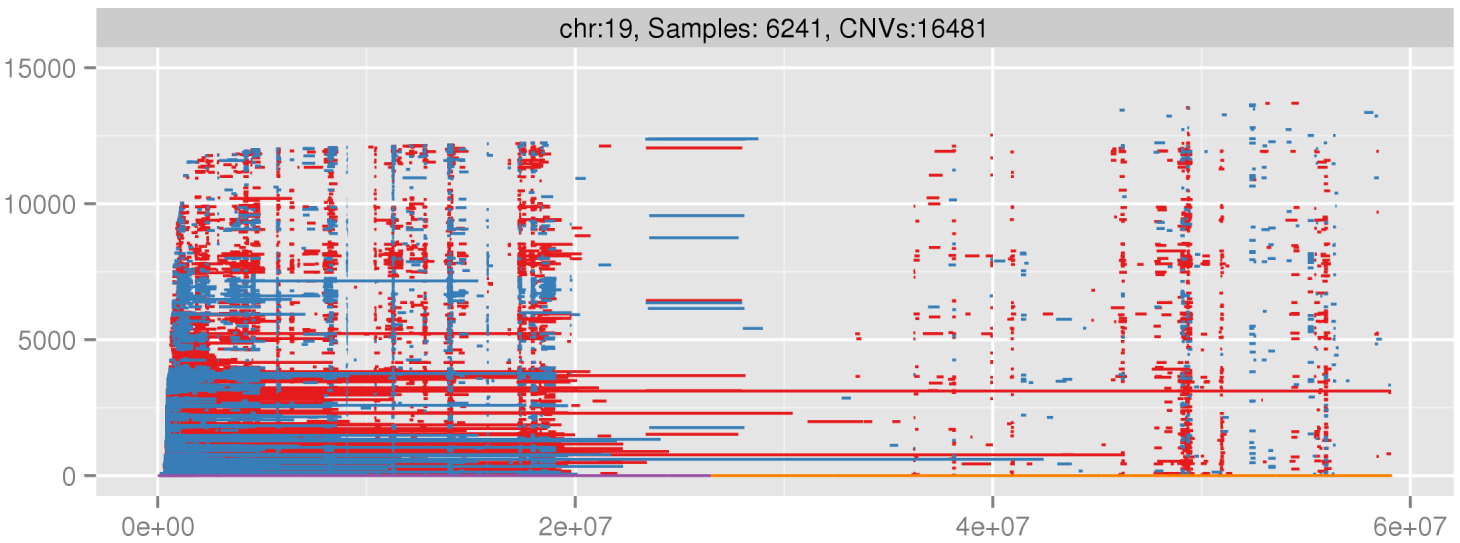
Example of false positives on chromosome 19 from PennCNV, specially on short arm (high GC content).

Amplified DNA from dried blood spots offers number of challenges for copy number of variation detection. Here we describe some of the challenges one can find working with DBS data.
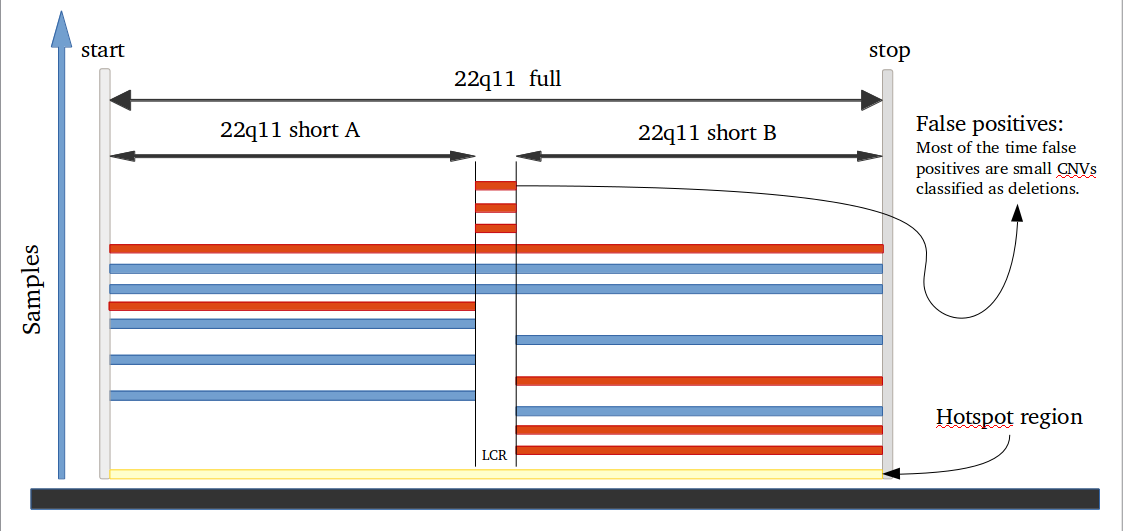
iPsychCNV package offers a series of tools that can be used in the CNV prediction pipeline, but also independent with other programs.
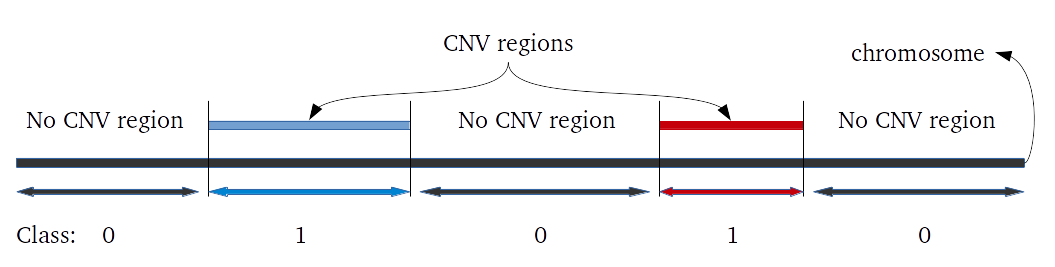
Evaluation of CNV prediction performance is an important step for methods comparison. Here we describe how binary classification is used to evaluate the method performance.
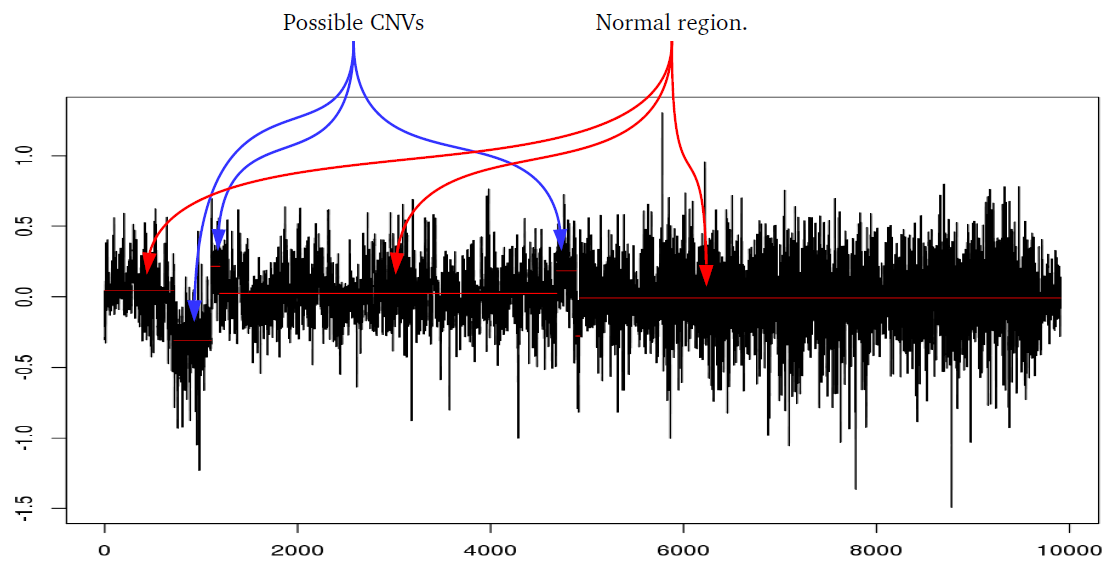
iPsychCNV uses many different methods to perform a series of functions. Here we describe in detail the methods used by iPsychCNV.